What HTTP really is?
If you ask a developer what is HTTP? he may respond (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) But we never spend time thinking about how it's working? or why it's working? HTTP is a protocol that runs over TCP/IP and it is responsible for carrying our code and defines how the code moves from the server to the client and how to decrypt that
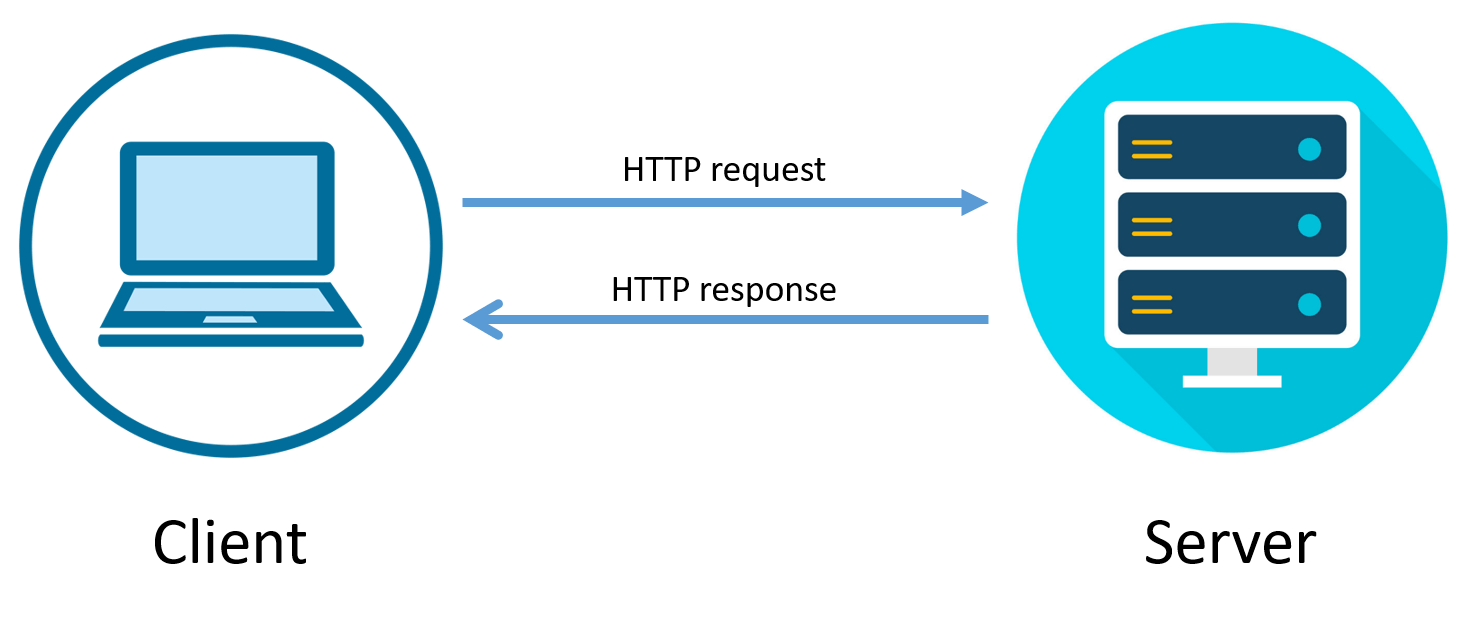
How HTTP Works?
An HTTP message (either a request or a response) contains multiple parts:
- start line
- headers
- body
HTTP requests
An HTTP request is a way internet communications platforms such as web browsers ask for the information they need to load a website.
Request Line
the request line indicates the verb used by the client, the path of the resource it wants, and the version of the protocol it is going to use.

In this case, the client is trying to GET the resource at the Request-URI through version 1.1 of the protocol.
Headers
Headers are text information stored in key-value pairs packets made up of data and metadata where the requests come form In this request, for example, the client has attached three additional headers to the request, Host, Accept, and we can add custom headers.
HTTP responses
the response header is simply what the server is sending you
 response contains:
response contains:
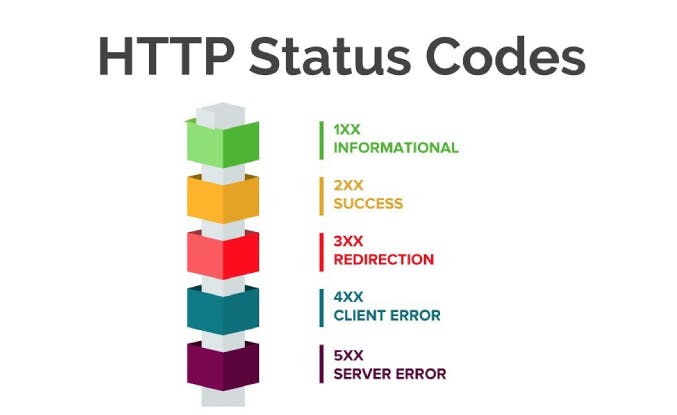
HTTP status code
HTTP response status codes indicate whether a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed. Responses are grouped into five classes:
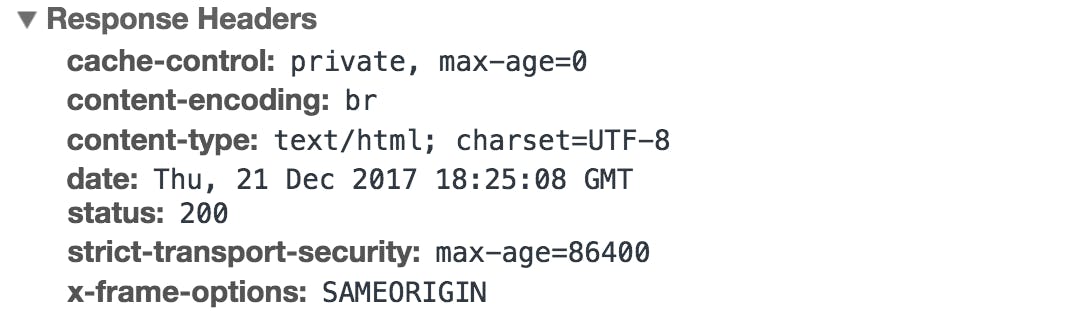
HTTP response headers
HTTP response headers convey important information such as the language and format of the data being sent in the response body.
optional HTTP body
Bodies can be broadly divided into three categories:
- Single-resource bodies, consisting of a single file of known length, are defined by the two headers:
Content-TypeandContent-Length. - Single-resource bodies, consisting of a single file of unknown length, encoded by chunks with
Transfer-Encodingset to chunked. Multiple-resource bodies, consisting of a multipart body, each containing a different section of information. These are relatively rare.